Beebotte BeeRules are trigger - condition - action rules that allow to create business logic on messages as they go through Beebotte network.
When Beebotte receives a message or an event corresponding to a BeeRule trigger, the BeeRule condition gets evaluated. If the condition is satisfied, then the BeeRule action is executed.
BeeRules allow to:
webhooks when specific events happenA BeeRule is composed of three parts: trigger, condition, and, action.
trigger can be any message or connection event including:
publish a message being published to a given channelwrite a message written to a given channel resourceconnect a WebSocket or MQTT client connection to a user's accountdisconnect a client disconnectionsubscribe a Websocket or MQTT subscription event to a channelunsubscribe an unsubscribe event from a channel/resourcejoin a Websocket subscription to a presence channelleave an unsubscribe event from a presence channelcondition optional condition to be satisfied in order for the rule's action to be executed. The condition is a true/false expression applied on the event data or metadata.
action an action to perform if the condition is satisfied. It can be one of:
write writes a message to a given Beebotte channel/resource.publish publishes a message to a given channel/resource.webhook calls a webhook on an external system. This enables integration with a wide set of applications.FCM publishes a data or a notification message to Firebase Cloud Messaging platform. This enables sending push notifications to Android and iOS devices.Email sends an email notification to a given address.BeeRules are triggered by events on the account. These events can be divided into:
publish and write messages on channel resources.subscribe, unsubscribe events on Websockets or MQTT connections and join and leave events on presence channels.BeeRule trigger is defined by three parameters: event, channel and resource.
The trigger event indicates the nature of the trigger. It can be one of the following:
publish a message being published to a given channelwrite a message written to a given channel resourceconnect a WebSocket or MQTT client connection to a user's accountdisconnect a client disconnectionsubscribe a Websocket or MQTT subscription event to a channelunsubscribe an unsubscribe event from a channel/resourcejoin a Websocket subscription to a presence channelleave an unsubscribe event from a presence channelThis is the channel the event was sent to. For example it can be the channel a message was published to or the channel a connection was subscribed to. The channel can be set to the wildcard character * to indicate any channel.
This is the resource the event was sent to. For example it can be the resource a message was written to or the resource a connection was subscribed to. The resource can be set to the wildcard character * to indicate any resource.
The BeeRule condition is an expression that gets evaluated every time an event matches the BeeRule trigger. If the BeeRule condition is satisfied (evaluates to true) then, the action of the BeeRule will be executed. The condition can therefore be considered as a filter on the BeeRule action execution.
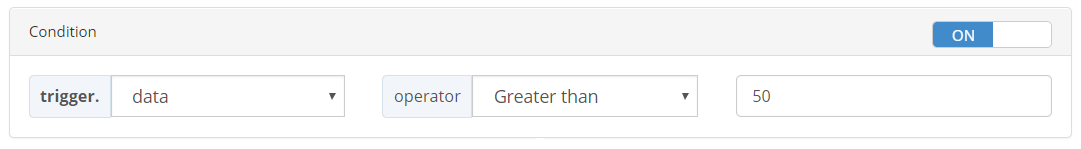
BeeRule conditions are optional, when not specified, the action part of the BeeRule will be executed every time a message matches the BeeRule trigger.
write and publish ActionsAs their name indicate, BeeRules with write or publish actions will write or publish a message to a channel resource.
When creating a BeeRule with write or publish action, the destination channel and resource must be defined.
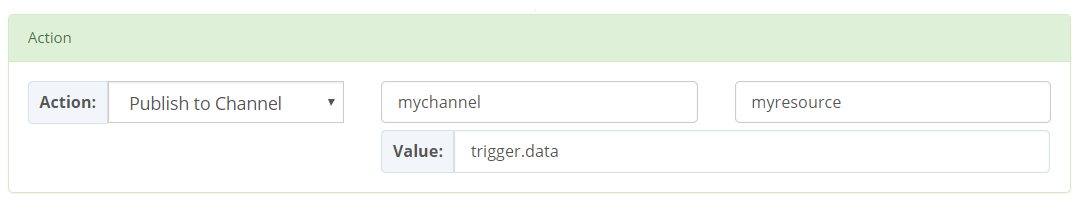
A special case when the value of channel or resource parameters of the action is set to trigger. In this case, it is a reference to the channel or resource form the trigger.
Email NotificationBeeRule Email action allows to send email notifications. Creating a BeeRule with Email action requires the following parameters:
mailto: the email address to send the notification to.
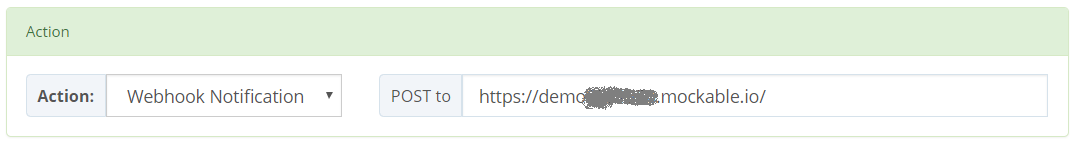
webhook ActionThe BeeRule webhook action will perform a POST request to the Webhook's endpoint.
The POST request data is a JSON defined as follows:
{
"timestamp": timestamp in milliseconds,
"type": "beerule",
"retries": number of retries,
"source": The BeeRule object,
"object": The trigger message
}
The following provides a concrete example of the POST request data of Webhook action.
{
"timestamp": 1548028108312,
"type": "beerule",
"retries": 0,
"source": {
"_id": "BEERULE_IDENTIFIER",
"lastModified": "2019-01-20T23:48:15.568Z",
"creationDate": "2019-01-20T23:48:15.568Z",
"name": "webhook beerule",
"description": "some description",
"condition": "channeltest.res1 > 0",
"owner": "beebotte",
"trigger": {
"event": "write",
"channel": "channeltest",
"resource": "res1"
},
"enabled": true,
"action": {
"endpoint": "https://demoxxxxxxx.mockable.io/",
"type": "webhook"
},
"__v": 0
},
"object": {
"data": 1,
"owner": "beebotte",
"channel": "channeltest",
"resource": "res1",
"event": "write",
"protocol": "rest"
}
}
FCM ActionBeeRule FCM action allows to publish notifications or data messages to Android and iOS devices. Creating a BeeRule with FCM action requires the following parameters:
to: the destination of the message on FCM. This is the value of the device token or the destination topic.isTopic: a boolean flag that indicates if the destination on FCM is a topic.isNotification: a boolean flag that indicates if a notification or a data message must be sent to FCM.value: expression that resolves to the object value that will be sent to FCM. By default, it is the trigger data.server key: the FCM server key that will be used to send messages to FCM.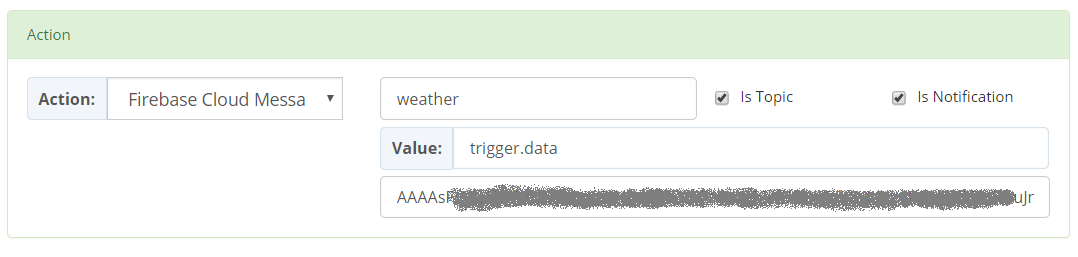
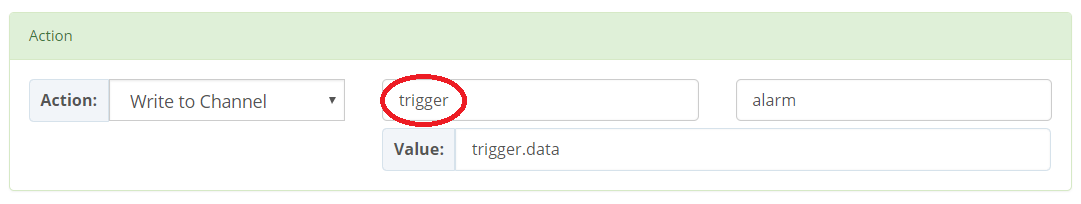
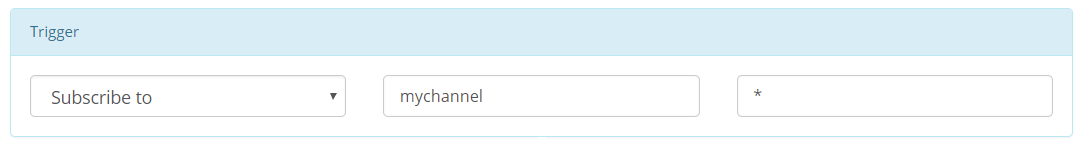
Consider you have a fleet of sensor devices and you want to raise an alarm whenever a sensor measures temperature above 50°. For every sensor, you have a channel and two resources temperature and alarm.
You can create a BeeRule as illstrated in the following screenshot:
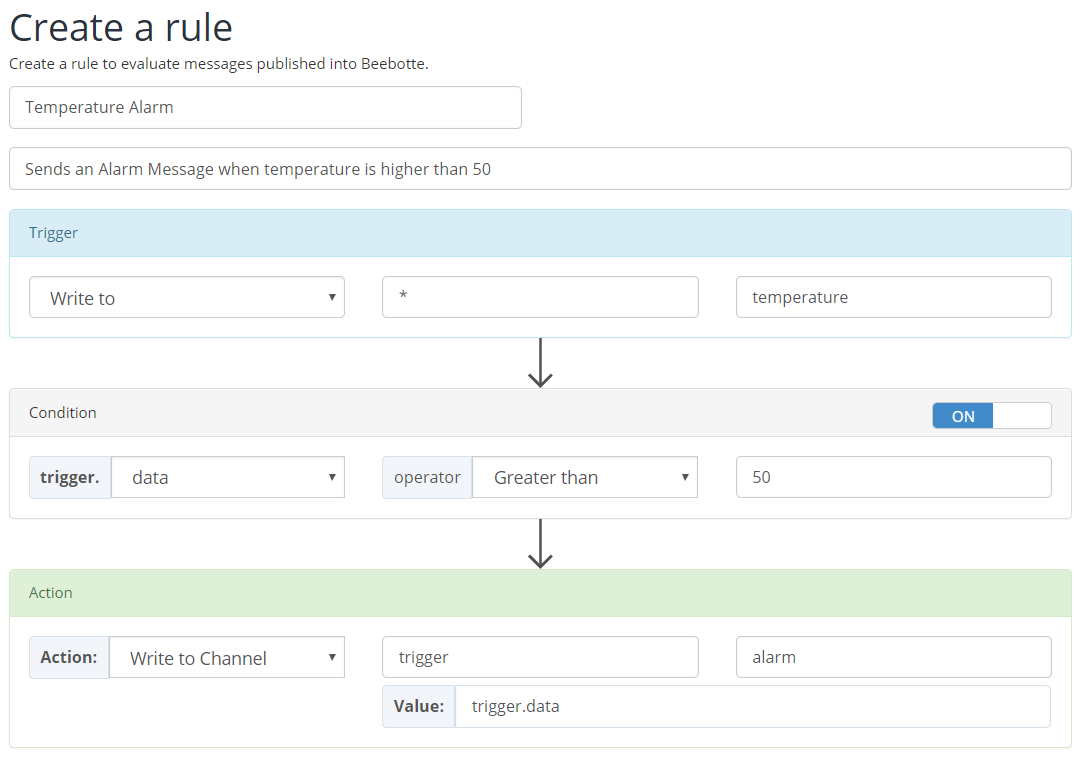
with:
write, channel set to wildcard * and resource temperature: this indicates that for every write message to any channel and resource temperature the trigger should be matched. This way, with one BeeRule, we cover all of our sensors.trigger.data greater than 50: this is exactly the condition to match. See how we are referring to the data by trigger.data; trigger here is a reference to the matched trigger message.connect or disconnect trigger events, the channel and resource should be set to NA. This is because connect and disconnect events are not channel based (a client do not connect to a channel).
A special case when channel or resource are set to one of clientid, sid or userid, then
the channel or resource value will be considered to be clientid, sid or userid of the trigger message.
Example: if the channel of connect trigger is set to clientid, then, the channel will be considered as the client id. This is only valid for connect or disconnect events.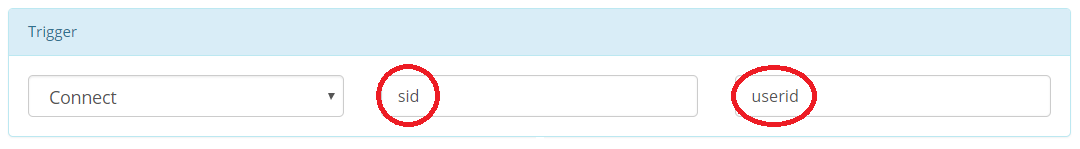
trigger as value of the channel or resource. As an example, a write action to channel trigger means a write to the same channel as that of the trigger.